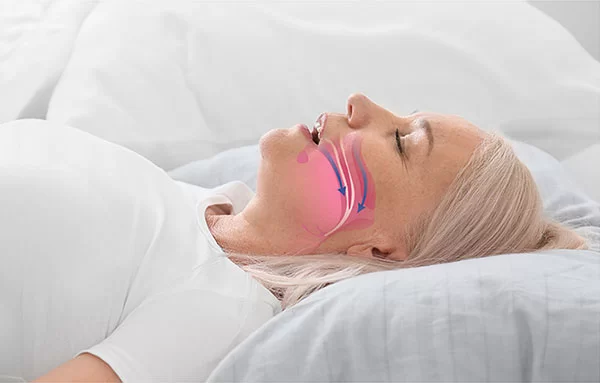
Is Your Snoring an Indicator of Sleep Apnea?
Sleep is essential for our overall well-being, and disturbances during sleep can have a significant impact on our health and quality of life. Two common sleep-related issues that often get confused are sleep apnea and snoring. While both can disrupt a good night’s sleep, they’re distinct conditions with different causes, symptoms, and consequences.
Our Wilmington and Seaford, DE, dentists break down the differences and similarities between sleep apnea and snoring, helping you better understand these sleep-related issues.
What Is Snoring?
Snoring is a common occurrence during sleep and is caused by the vibration of tissues in the throat as a person breathes. Snoring itself is not a sleep disorder but rather a symptom of airway obstruction or resistance to airflow during sleep.
The primary symptom of snoring is the sound produced during sleep. While many snorers don’t experience any significant issues related to their snoring, it can be disruptive to bed partners and occasionally indicate underlying sleep apnea.
What Causes Snoring?
Snoring can be caused by various factors, including:
- Obesity
- Enlarged tonsils or adenoids
- Nasal congestion
- Sleeping position
- Alcohol and sedative use
- Age-related muscle relaxation
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These pauses in breathing, known as apneas, can last for seconds to minutes and can occur multiple times during the night.
There are two primary types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common type of sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, leading to the narrowing or complete closure of the airway.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): CSA is less common and results from a failure of the brain to transmit the proper signals to the muscles responsible for controlling breathing.
Sleep Apnea Symptoms
Common symptoms of sleep apnea include:
- Loud snoring
- Pauses in breathing during sleep
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Morning headache
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
Differences Between Snoring and Sleep Apnea
There are a few distinguishing factors between sleep apnea and snoring, including:
- Nature: Sleep apnea involves pauses in breathing during sleep, while snoring is the noisy vibration of tissues during breathing.
- Consequences: Sleep apnea can lead to serious health issues, including cardiovascular problems, whereas snoring is generally considered a nuisance.
- Diagnosis: Sleep apnea is diagnosed through sleep studies, while snoring is typically diagnosed based on the sound produced during sleep.
- Treatment: Treatment for sleep apnea may involve lifestyle changes, devices like CPAP machines, or surgery. Snoring management often includes lifestyle modifications and devices like snoring mouthpieces.
- Symptoms: Sleep apnea is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness, while snoring may not cause significant daytime symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Sleep Apnea
- Diagnosis: Sleep apnea is typically diagnosed through a sleep study (polysomnography) that monitors various aspects of your sleep, including breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and brain activity.
- Treatment: Treatment options for sleep apnea include lifestyle changes (weight loss, positional therapy), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, oral appliances, surgery (for severe cases), and addressing underlying medical conditions.
Snoring
- Diagnosis: Snoring is often diagnosed based on a physical examination and a discussion of symptoms. In some cases, a sleep study may be recommended to rule out sleep apnea.
- Treatment: Snoring can be managed through lifestyle changes (weight loss, avoiding alcohol and sedatives), positional therapy (changing sleep position), and using snoring mouthpieces or nasal strips.
Frequently Asked Questions
While snoring itself is not a direct cause of sleep apnea, it can be a symptom or warning sign of sleep apnea. A healthcare professional should evaluate loud and persistent snoring.
Yes, there are natural remedies for snoring, such as weight loss, changing sleep position, and using saline nasal sprays to alleviate congestion. Lifestyle modifications can often reduce snoring.
Yes, children can have sleep apnea, which is often associated with enlarged tonsils or adenoids. It’s important to identify and treat pediatric sleep apnea to prevent long-term health issues.
Know When to Seek Treatment for Sleep Apnea
If you snore, it’s best to seek a sleep apnea evaluation. While snoring doesn’t always mean you have a sleep disorder, it’s always best to rule it out. To learn more, contact us today by calling our Wilmington office at (302) 999-7600 or our Seaford office at (302) 536-7589. We proudly provide comprehensive dental services to Pike Creek, Marshallton, and Stanton, DE, patients.